
In the 1800s, James Clerk Maxwell discovered that there is an important relationship between electric and magnetic fields. So, what does the word ‘electromagnetic’ mean anyway? Is it electric? Is it magnetic? All electromagnetic waves are composed of both electric and magnetic fields that oscillate at right angles to each other. The various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation range from about 108 meters down to 10-16 meters. The velocity of an electromagnetic wave is generally constant for a given medium that it is traveling through. For example, gamma rays have the highest frequencies and the shortest wavelengths, while radio waves have the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths. This means that if one increases, the other must decrease. This equation shows the inverse relationship between the wavelength and the frequency. Where v is the velocity of the wave, λ is the wavelength, and f is the frequency. The relationship between wavelength and frequency for a wave is described by a simple equation: The amount that it slows down depends on the material and how energetic the wave is.

In a vacuum, these waves all travel at the speed of light, c, which is roughly 300,000 kilometers per second faster than anything else in the universe! However, when light is traveling through air, water, or any other material, it slows down. The frequency can be thought of as the number of oscillations per second or the number of crests or troughs that pass a certain point per second. The wavelength of a light wave is considered to be the distance from crest to crest or trough to trough where the trough is the lowest part of the wave and the crest is the highest. Beyond that are infrared, microwave, and radio waves with the lowest energy end of the spectrum.Īll of these types of radiation act as waves with a wavelength, measured in meters, and a frequency, measured in units of Hz or cycles per second. Violet light has the highest energy (just below ultraviolet) and red light has the lowest energy. Next up is visible light, which is just the range of the spectrum that human eyes are able to detect. The highest-energy part of the spectrum consists of gamma rays and as you go down in energy, you find x-rays and then ultraviolet light, which is the radiation that causes sun burns.
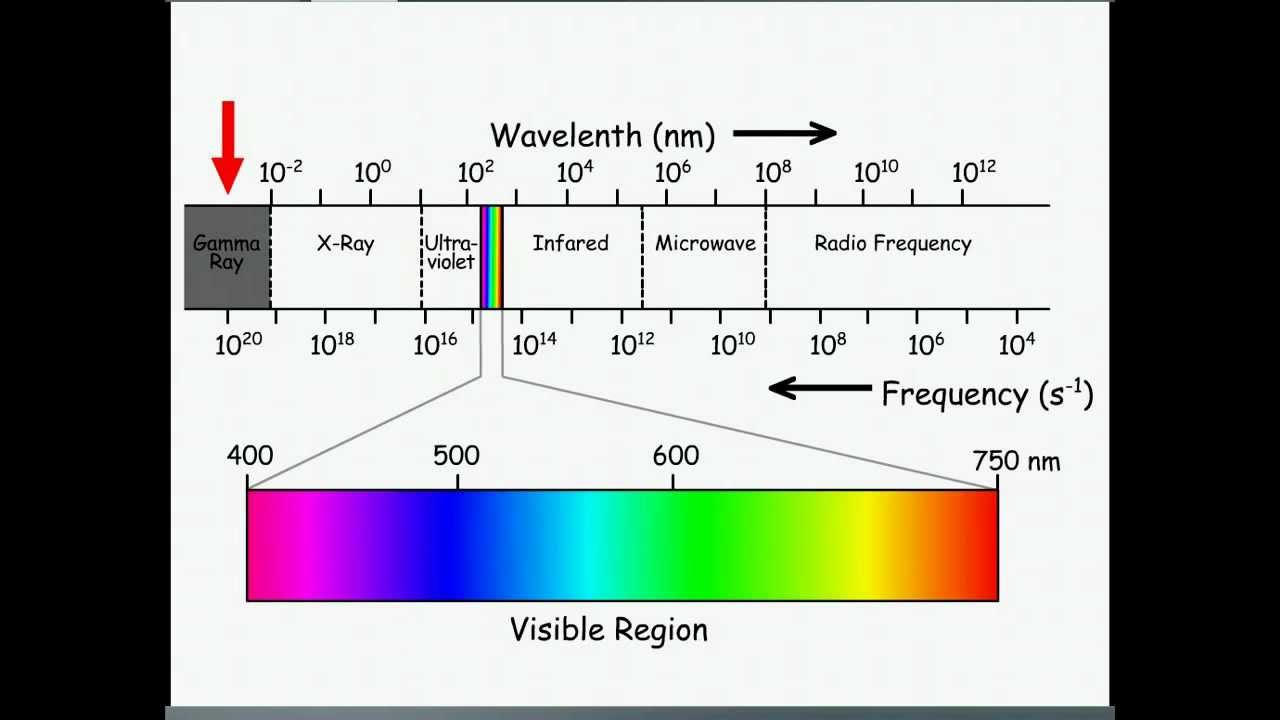
If you take that rainbow of colors and expand it out past visible light on both ends, you’ll eventually end up with the whole electromagnetic spectrum. You may be familiar with the color spectrum of a rainbow this is actually just a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Though we use the term radiation, only the higher-energy electromagnetic waves are dangerous because they are able to penetrate cells more easily. All of these forms of radiation contain varying amounts of energy. The electromagnetic spectrum is what we call all of the forms of electromagnetic radiation that travel at the speed of light while in a vacuum. You may have heard of the electromagnetic spectrum, but what, exactly, does that encompass, and why is it electromagnetic? Hi, and welcome to this video on the electromagnetic spectrum! In this video, we’ll discuss what the electromagnetic spectrum is and go over the properties of electromagnetic waves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
